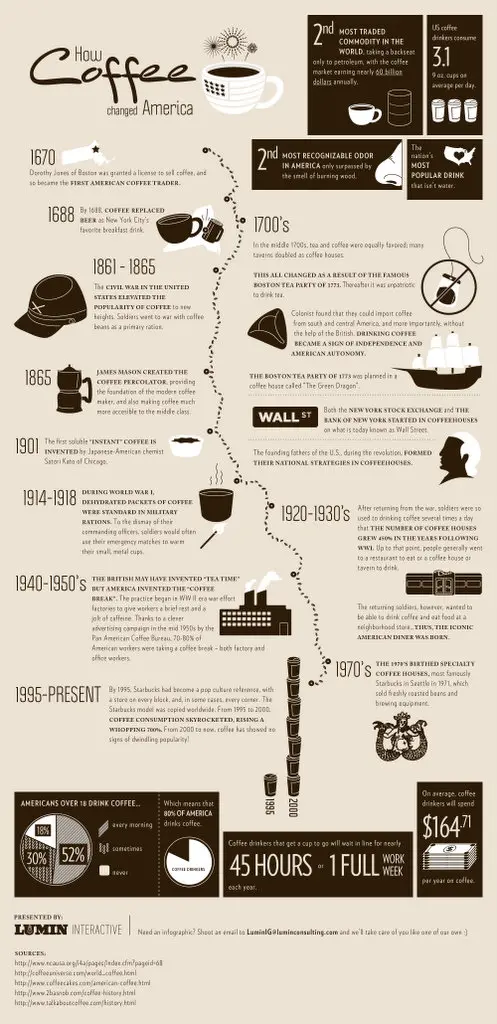
For millions of people around the world, coffee is the fuel that kickstarts their day. The aromatic brew has become a daily ritual for many, providing a much-needed boost of energy and mental alertness. But have you ever wondered how coffee affects your brain? Let's delve into the science behind this beloved beverage and explore its fascinating impact on the most complex organ in our bodies.

Caffeine, the primary active ingredient in coffee, is a natural stimulant that belongs to a class of compounds known as methylxanthines. When consumed, caffeine quickly makes its way to the brain and begins to work its magic. One of the key mechanisms of caffeine is blocking adenosine receptors in the brain. Adenosine is a neurotransmitter that promotes relaxation and drowsiness. By binding to these receptors, caffeine prevents adenosine from having its sedative effect, leading to increased wakefulness and alertness.
The effects of coffee on the brain are widespread and varied. One of the most noticeable impacts is an improvement in mental focus and attention. Caffeine stimulates the release of neurotransmitters like dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin, which play crucial roles in regulating mood, motivation, and cognitive function. These neurotransmitters enhance communication between neurons, leading to heightened concentration and improved reaction time. This can be particularly beneficial when faced with demanding mental tasks or when trying to stay sharp during long study or work sessions.
Coffee's influence extends beyond the short-term focus. Studies have shown that regular coffee consumption can have long-term effects on brain health. Research suggests that coffee may help protect against neurodegenerative disorders like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease. The exact mechanisms behind this protective effect are not yet fully understood, but it is believed that coffee's antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, along with its ability to enhance brain plasticity and reduce the accumulation of harmful proteins, may contribute to these benefits.
Moreover, coffee has been linked to improved cognitive function and a reduced risk of cognitive decline. Studies have found that individuals who regularly consume coffee exhibit better memory, attention, and executive function compared to non-coffee drinkers. The presence of bioactive compounds in coffee, such as chlorogenic acids and caffeine, may be responsible for these cognitive benefits. These compounds have been shown to have positive effects on cerebral blood flow, neuronal activity, and the formation of new brain cells.

While coffee has many positive effects on the brain, it is essential to understand that individual responses to caffeine can vary. Some people are more sensitive to its effects and may experience jitters, anxiety, or sleep disturbances with higher doses. It is crucial to find the right balance of coffee consumption that works best for you. Additionally, tolerance to caffeine can develop over time, requiring higher doses to achieve the same level of alertness. It's advisable to moderate your intake and avoid excessive consumption, especially in the hours leading up to bedtime.
Coffee is much more than a delightful beverage. Its active ingredient, caffeine, affects the brain in various ways, enhancing mental focus, promoting wakefulness, and potentially protecting against neurodegenerative diseases. Regular coffee consumption has been associated with improved cognitive function and a reduced risk of cognitive decline. However, it's essential to remember that moderation is key, as individual responses to caffeine can vary. So, the next time you savor that cup of coffee, appreciate the intricate dance between this aromatic elixir and your brain, and enjoy the cognitive boost it provides.